Java is truly an amazing programming language. And among its rich toolkit, Spring Boot definitely stands out as a powerful building block. With Spring Boot, we build fast, effective, and sustainable applications. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the core layers of Spring Boot: Controller, Service, and Repository annotations.
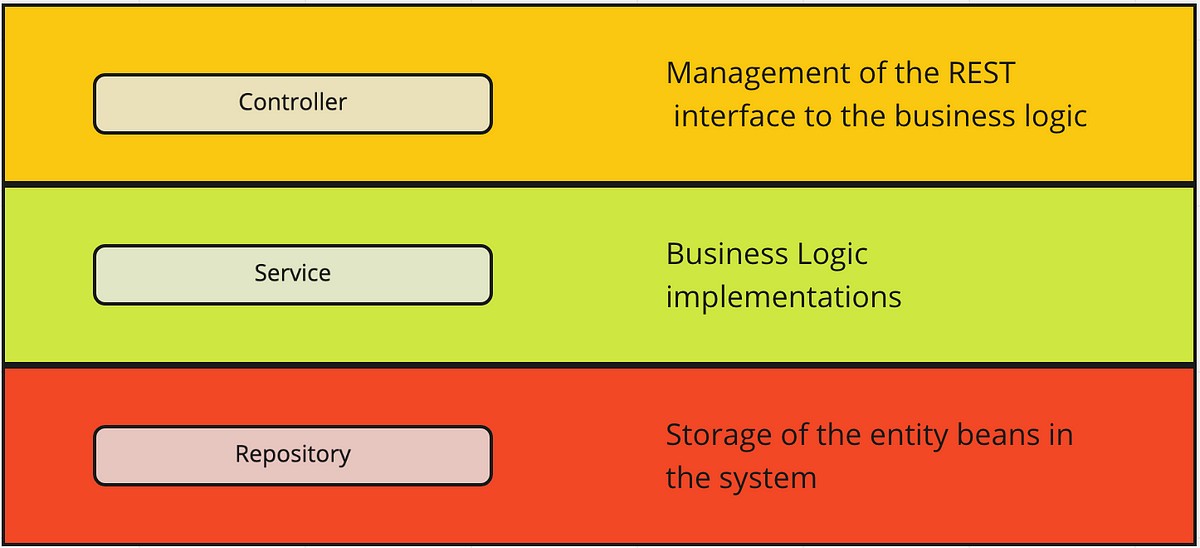
Why Layered Architecture? #
Before jumping in, let’s quickly understand why layered architecture matters:
- Separation of concerns: Makes code easier to read and maintain.
- Testability: Each layer can be tested independently.
- Reusability: Business logic can be reused in different parts.
- Scalability: Easier to extend and modify.
Controller #
Controller is the layer that handles incoming HTTP requests. It listens to what the client asks for and directs the request to the appropriate handler. When building REST APIs, we usually use @RestController which automatically returns JSON or XML responses.
We handle HTTP requests using @RequestMapping or its shortcuts like @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, and @DeleteMapping.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<UserDto> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
UserDto user = userService.getUserById(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<UserDto> createUser(@RequestBody UserDto userDto) {
UserDto createdUser = userService.createUser(userDto);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(createdUser);
}
}
Service #
The Service layer is where the business logic lives. Data coming from the controller is processed here — validations, calculations, and any rules specific to the domain are handled in this layer. It’s the brain of the application.
Marking a class with @Service lets Spring recognize it as a service component and automatically inject it where needed.
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
public UserDto getUserById(Long id) {
User user = userRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new EntityNotFoundException("User not found"));
return convertToDto(user);
}
public UserDto createUser(UserDto userDto) {
User user = convertToEntity(userDto);
User savedUser = userRepository.save(user);
return convertToDto(savedUser);
}
}
Repository #
Repository is the data access layer, responsible for communicating with the database. Usually defined as an interface extending Spring Data interfaces like JpaRepository or CrudRepository.
CrudRepositoryprovides basic CRUD operations.JpaRepositoryextends CrudRepository and also offers pagination and sorting support.
You can also write custom queries using the @Query annotation when standard methods aren’t enough.
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
List<User> findByLastName(String lastName);
@Query("SELECT u FROM User u WHERE u.email = :email")
Optional<User> findByEmail(@Param("email") String email);
}
How These Layers Work Together #
A typical request flow goes like this:
- Client sends an HTTP request.
- Controller receives the request and extracts data.
- Controller calls the Service layer.
- Service processes the business logic and calls the Repository layer.
- Repository interacts with the database.
- Service returns processed data back to the Controller.
- Controller sends the response to the client.
Summary #
| Layer | Responsibility | Annotations | Example Interfaces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controller | Handles HTTP requests & routing | @RestController |
- |
| Service | Implements business logic | @Service |
- |
| Repository | Manages data access | @Repository |
JpaRepository, CrudRepository |
Conclusion #
Using layered architecture with Controller, Service, and Repository in Spring Boot helps you write code that is clean, testable, and maintainable. These annotations clearly separate responsibilities, making your application easier to build and evolve.